Summary
Article Name
History of Drones in Warfare
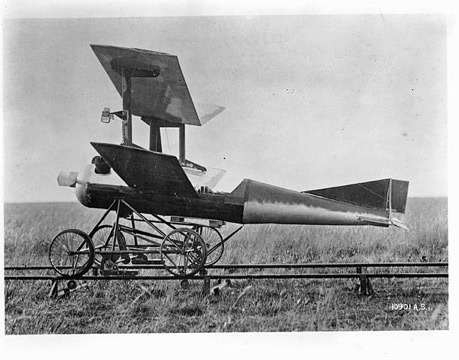
DescriptionThe concept of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Early experiments involved balloon bombs, such as the ones used by Austria against Venice in 1849, though these were primitive and not guided.
Author
Manas Verma
Publisher Name
MachOne Advisors
Publisher Logo




